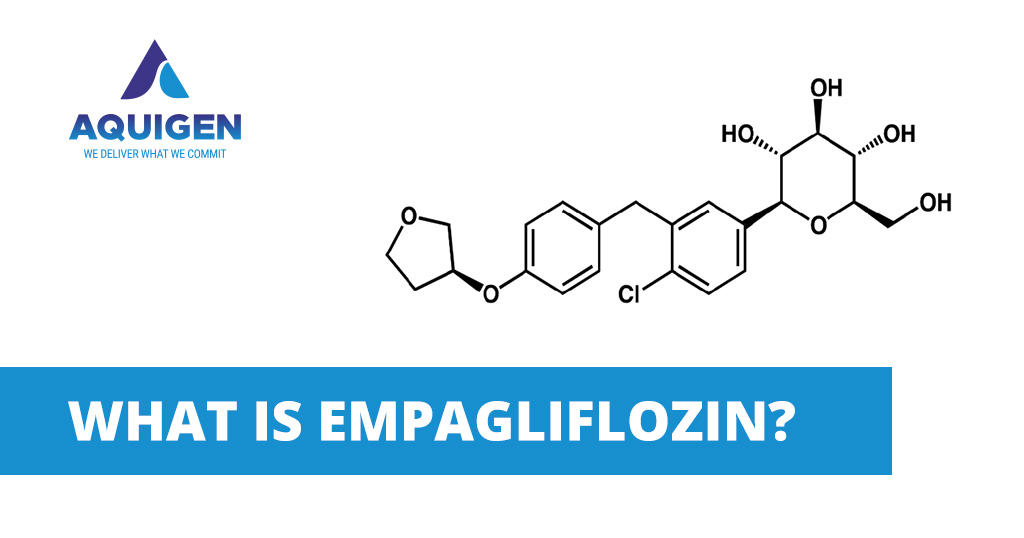
Empagliflozin is an important antidiabetic drug used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It works by selectively and reversibly inhibiting SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) present in the proximal convoluted tubule of kidneys. SGLT2 is responsible for reabsorbing around 90% of the filtered glucose back into the bloodstream. By blocking this transporter, Empagliflozin prevents the reabsorption of filtered glucose and helps eliminate it via urine. This unique mechanism of action helps lower blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Launched in 2014, Empagliflozin was the first in its class of antidiabetic drugs known as SGLT2 inhibitors. Other similar drugs approved later include Canagliflozin, Dapagliflozin, Ertugliflozin etc. Empagliflozin offers benefits beyond glycemic control alone. It has shown results in reducing cardiovascular as well as renal complications in diabetic patients, especially in those with existing cardiovascular problems. This makes Empagliflozin a valuable option in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and warrants a closer look at its clinical profile and applications. At Aquigen Bio Sciences, we provide Empagliflozin Impurities and Synthesis. Let’s learn more about this significant diabetes drug in detail.
Mechanism of Action- Empagliflozin
Empagliflozin is a member of the SGLT2 inhibitor class. SGLT2 is present in the proximal convoluted tubule of the kidneys and is responsible for reabsorbing the majority of glucose filtered through the glomeruli back into the bloodstream. Empagliflozin selectively and reversibly inhibits SGLT2 and prevents the reabsorption of filtered glucose, increasing urinary glucose excretion. This helps lower the blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Indications
Empagliflozin is primarily indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is used alone or in combination with other antidiabetic medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors etc. Empagliflozin has also shown benefits in reducing cardiovascular and renal complications in diabetes patients with established cardiovascular disease.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage of Empagliflozin is 10 mg or 25 mg once daily, taken orally with or without food. The dose can be increased to 25 mg for better glucose control if tolerated. Empagliflozin is available as film-coated tablets of 10 mg and 25 mg strengths.
Impurities Profile
During the synthesis and stability studies of Empagliflozin, several process-related and degradation impurities are reported. The key Empagliflozin Impurities include starting materials, intermediates, byproducts, and degraded products. Empagliflozin Impurities Manufacturers like Aquigen Bio Sciences specialize in providing reference standards for these impurities to support drug development and manufacturing of Empagliflozin.
Some important impurities seen during the synthesis of Empagliflozin are:
- Diketopiperazine impurity
- Acetamide impurity
- Lactam impurity
- Unsaturated lactam impurity
Safety and Side Effects
Empagliflozin is generally well tolerated by most patients. However, some common side effects have been reported which include genital fungal infections like candidiasis. This occurs more often in female patients. Other minor side effects include symptoms of urinary tract infections like dysuria, increased urination or polyuria.
More serious but rare side effects involve a condition called ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. Patients on a high carbohydrate diet or during periods of illness/surgery seem to have a slightly higher risk of ketoacidosis with Empagliflozin intake. Therefore, diabetic ketoacidosis is considered a potential risk, especially in type 1 diabetes where insulin may be deficient.
Given its mechanism of action involves excessive urinary glucose excretion, Empagliflozin must be used cautiously or avoided in patients with severe impairment of kidney function. It is not recommended for individuals suffering from end-stage renal disease. Close monitoring of renal parameters is advisable when prescribing Empagliflozin to patients with mild to moderate renal insufficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Empagliflozin is an important drug for the management of type 2 diabetes. As a leading Empagliflozin Impurities Manufacturer, Aquigen Bio Sciences offers high-quality reference standards of all process-related and degradation impurities to support quality manufacturing and research activities. We are proudly known for our expertise in impurity synthesis and purification. Researchers can rely on us for their empagliflozin impurities synthesis and analytical requirements. Feel free to get in touch and share your empagliflozin impurities requirements.