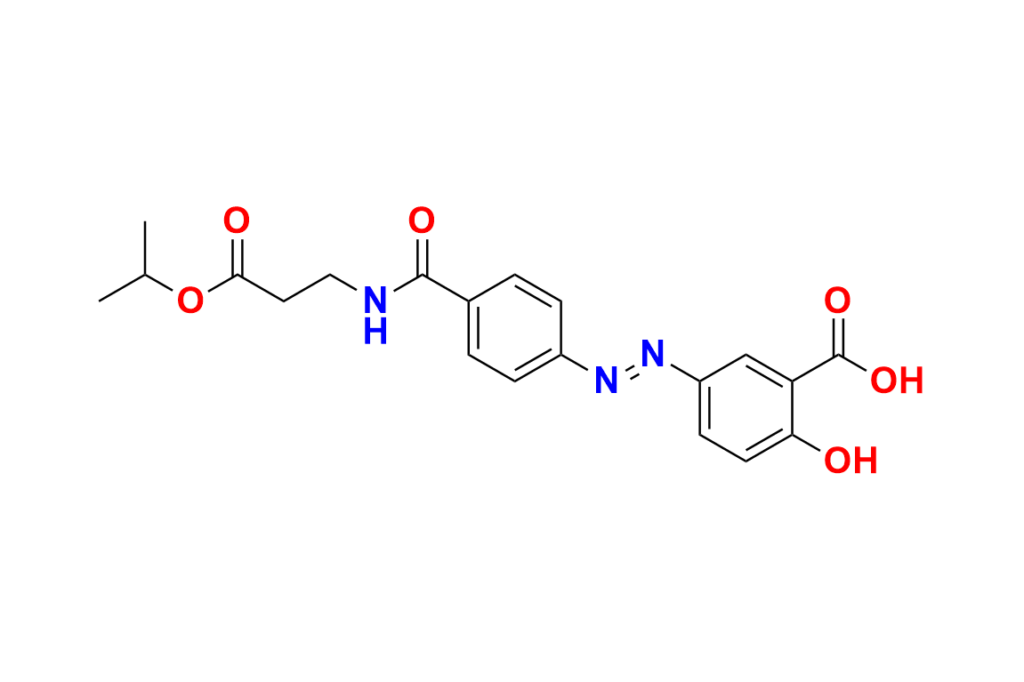
Balsalazide USP Impurity 5
In Stock
| CAT NO | AQ-B000516 |
|---|---|
| CAS NO | 1346606-13-0 |
| Mol.F | C20H21N3O6 |
| Mol.Wt | 399.4 |
| Availability | In Stock |
| Chemical name | 2-Hydroxy-5-((4-((3-isopropoxy-3-oxopropyl)carbamoyl)phenyl)diazenyl)benzoic acid |
Ready To Dispatch Within 24 Hours
In Stock
Request for Quotation :
Balsalazide USP Impurity 5
Product Description
Balsalazide USP Impurity 5 is a high-quality reference standard supplied with comprehensive characterization data, ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines. This product is essential for analytical method development, method validation (AMV), quality control (QC) applications, and plays a crucial role in Abbreviated New Drug Applications (ANDA).
Balsalazide USP Impurity 5 can be used as a reference standard, with possible traceability to pharmacopeial standards such as USP or EP, based on feasibility. AquigenBio products are strictly for analytical purposes and is not intended for human use.
Applications of Balsalazide USP Impurity 5:
1. Pharmaceutical Impurity Profiling
-
Balsalazide USP Impurity 5 is a recognized compendial impurity associated with Balsalazide API and its formulations.
-
It is used to identify, quantify, and monitor known related substances to ensure drug purity, stability, and regulatory compliance.
2. Analytical Method Development & Validation
-
Acts as a certified reference standard for the development of analytical methods such as:
-
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
-
Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC)
-
LC-MS/MS
-
-
Essential for validating:
-
Specificity
-
Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
-
Accuracy, precision, and linearity
-
3. Regulatory Submissions (ICH & USP Compliance)
-
Used to meet regulatory requirements under:
-
ICH Q3A/B guidelines for impurity qualification
-
USP monographs for Balsalazide drug substances
-
-
Included in:
-
ANDA (Abbreviated New Drug Application)
-
Drug Master Files (DMF)
-
Common Technical Documents (CTD) for global health authorities
-
4. Stability Studies & Degradation Analysis
-
Applied in forced degradation and long-term stability studies to:
-
Trace formation of known degradation products over time
-
Establish impurity pathways and assess formulation robustness
-
5. Routine Quality Control (QC) Testing
-
Used in batch release testing and in-process quality control to ensure impurity levels remain within acceptable regulatory limits.
-
Supports lot-to-lot consistency and product safety.
6. Research & Development (R&D)
-
Supports scientific investigation in:
-
Impurity mechanism studies
-
Synthetic route optimization
-
Reference standard comparison
-
Used by pharmaceutical labs, CROs, and academic researchers
-
⚠️ Note: This impurity standard is intended strictly for laboratory and analytical use only. Not for human or veterinary drug use.
Safety & Handling Information for Chemical Products
1. Read the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) : The SDS contains important safety information for handling procedures, first-aid measures, disposal instructions, etc. Read it carefully.
2. Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) : Always wear PPE as indicated in the SDS and by the manufacturer. This may include safety goggles, gloves, lab coats, respirators, and protective clothing.
3. Handle with Care : Be careful with chemical products - prevent spills, splashes, or inhaling fumes or dust. Use secondary trays or spill kits during chemical transfer or dispensing.
4. Work in a Well-Ventilated Area : Use chemical products in well-ventilated spaces to reduce vapour or gas exposure. Indoors, ensure ample ventilation via mechanical systems, fume hoods, or open windows and doors.
5. Avoid Mixing Chemicals : Avoid mixing chemical products unless directed by the manufacturer or a qualified professional. Incompatible mixes can lead to hazardous reactions, toxic gas releases, or explosions.
6. Labeling and Storage : Label chemical containers with product names, hazards, and handling information. Store in original or approved containers.
7. Prevent Contamination : Prevent cross-contamination with dedicated equipment or thorough decontamination. Keep food, drinks, and personal items away from chemical storage or work zones.
8. Emergency Procedures : Learn emergency procedures for spills, leaks, fires, or exposure incidents. Keep spill control materials, fire extinguishers, and emergency eyewash/shower facilities accessible.
9. First Aid : Know first aid for chemical exposure (eye contact, skin contact, inhalation, and ingestion). Ensure accessible supplies and trained personnel for assistance.
10. Proper Waste Disposal : Ensure chemical waste disposal as per local regulations; segregate hazardous from non-hazardous waste for health and environmental protection.
11. Training and Education : Offer thorough training to chemical handlers, covering usage, hazards, safety, and emergency response.
12. Report Incidents and Near Misses : Report incidents, near misses, spills, or safety concerns promptly to authorities and supervisors for investigation and action. By following these safety and handling guidelines, you can minimize risks associated with chemical products and create a safer work environment for yourself and others.
Read more
Wash thoroughly after handling. Remove contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. Avoid ingestion and inhalation.